本文档主要介绍如何利用Python和钉钉机器人实现智能运维。
利用Python可以很方便的监控服务器CPU、内存、硬盘等资源实时使用情况,通过服务器健康地址定时访问可以掌握服务器的在线情况,一旦出现故障,可以第一时间获得通知,并及时修复。
服务端 钉钉端
Python脚本运行 ———————————————–》故障消息提醒
发现故障,发送消息
创建钉钉机器人
钉钉中创建一个运维群,点击『群设置』,选择『机器人』,在弹出的『机器人管理』中,点击“添加机器人”,在弹出的机器人窗口中,点击“添加机器人”,选择“自定义”类型的机器人:
点击“添加”: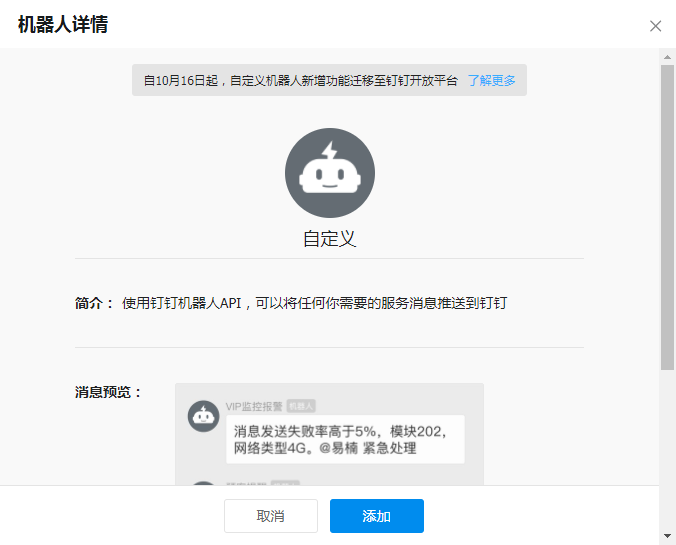
配置机器人信息: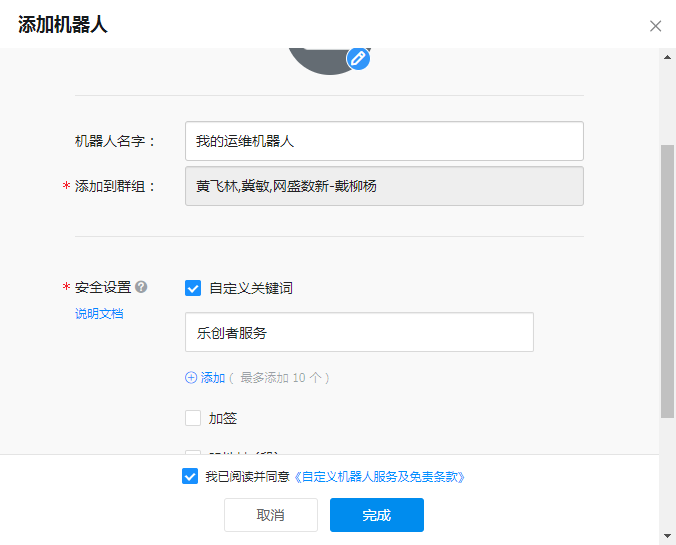
录入机器人名字,然后再安全配置中,勾选“自定义关键词”,并录入关键词信息(录入的内容必须在给钉钉机器人发送信息内容中包含),如:乐创者服务。
然后,勾选“我已阅读并同意《自定义机器人服务及免责条款》”,点击“完成”后,在机器人管理中即可看到此机器人。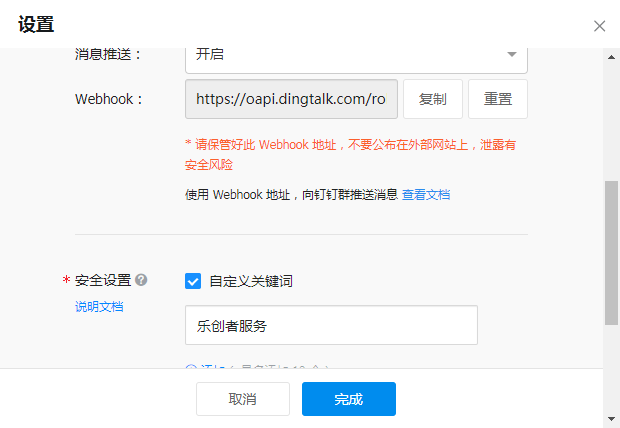
点击此机器人,进入设置窗口,复制出WebHook地址备用。
服务端部署Python环境
在需要智能监控的服务器上,需要安装Python环境。
在Pythonwindows上安装很简单,选择合适的版本即可,这里不介绍。
linux下,可按照以下部件进行安装(推荐使用Python3):
下载安装包(https://www.python.org/ftp/python/3.9.9/Python-3.9.9.tgz),并放到usr/src目录下:
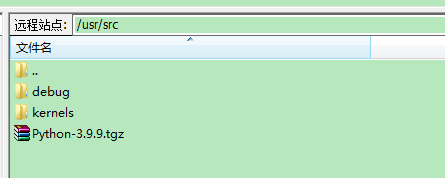
编译和安装Python3(分别执行以下命令):
tar -zxvf Python-3.9.9.tgz cd Python-3.9.9 ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/python3 --with-ssl make && make install创建软链接
ln -s /usr/local/python3/bin/python3 /usr/bin/python3
ln -s /usr/local/python3/bin/pip3 /usr/bin/pip3安装依赖插件:
pip3 install psutil pip3 install requests
编写脚本
按照需要监控的服务器信息,编写脚本(以下为示例代码,了解Python的用户可自行编写):
#-*- coding : utf-8 -*-
# coding:unicode_escape
import psutil
import requests
import json
import time
cpu_out_count = 0 #cpu连续次数
mem_out_count = 0 #memory连续次数
health_dis_count = 0 #健康地址失败连续次数
#向机器人发送文本消息通知
def send_message(content):
#print(content)
webhook_url = "https://oapi.dingtalk.com/robot/send?access_token=xxxxxxxxxxxxxx" #替换为对应钉钉机器人的Webhook
headers = {"Content-Type": "application/json;charset=utf-8"}
message = {"msgtype": "text", "text": {"content": content}}
res = requests.post(webhook_url, headers=headers, data=json.dumps(message))
return res
#cpu使用情况监控,超过预设值指定次数则向机器人发送消息通知
def monitor_cpu():
global cpu_out_count
cpu_percent = psutil.cpu_percent(interval=1)
if cpu_percent >= 85:
if cpu_out_count >= 2: #超过60s CPU占用都超过了
cpu_out_count = 0
content = "[乐创者服务]服务器CPU使用率 >= 85%,当前使用率为{},请及时关注!!!".format(cpu_percent)
send_message(content)
else:
cpu_out_count = cpu_out_count + 1
else:
cpu_out_count = 0
#硬盘使用情况监控,超过预设值指定次数则向机器人发送消息通知
def monitor_disk():
partition_usage = psutil.disk_usage("E:")
if partition_usage.percent >= 80:
content = "[乐创者服务]服务器磁盘空间已使用超过80%,当前使用率为{},请及时关注!!!".format(partition_usage.percent)
send_message(content)
#内存使用情况监控,超过预设值指定次数则向机器人发送消息通知
def monitor_memory():
global mem_out_count
mem = psutil.virtual_memory()
if mem.percent >= 85:
if cpu_out_count >= 2: #超过60s 内存占用都超过了
mem_out_count = 0
content = "[乐创者服务]服务器内存已占用超过85%,当前占用率为{},请及时关注!!!".format(mem.percent)
send_message(content)
else:
mem_out_count = mem_out_count + 1
else:
mem_out_count = 0
#服务器健康地址访问,不通则向机器人发送消息通知
def monitor_server():
global health_dis_count
health_url = "http://127.0.0.1:8081/lczServer/oapi/server/connectTestting" #乐创者服务健康地址
health_headers = {"Content-Type": "application/json;charset=utf-8"}
try:
res = requests.get(health_url, headers=health_headers)
if res.status_code != 200:
print(res.status_code)
if health_dis_count >= 4:
health_dis_count = 0
send_message('[乐创者服务]服务健康地址访问返回状态码不是200,请及时关注!!!')
else:
health_dis_count = health_dis_count + 1
else:
health_dis_count = 0
except Exception as e:
health_dis_count = health_dis_count + 1
if health_dis_count >= 10:
health_dis_count = 0
send_message('[乐创者服务]服务健康地址访问不通,请及时关注!!!')
#定义gongzuo内容
def do_work():
while True:
time.sleep(30) #暂停30秒后开始工作
print("当前时间:%s" % time.ctime())
monitor_cpu()
monitor_memory()
monitor_server()
monitor_disk()
#主入口
if __name__ == "__main__":
do_work()
运行监控
windows服务
请下载附件Python_windows.rar文件,解压缩后,打开说明.txt文件进行操作。
Linux服务
将下载附件Python_linux.rar文件,解压缩后,将lczServerWatchmen.py上传到/usr/local/lczServerMonitor目录下,执行以下命令,开始监控:
cd /usr/local/lczServerMonitor
python3 lczServerWatchmen.py最后编辑:柳杨 更新时间:2025-09-03 16:32
 扫码关注网盛数新公众号,获取更多帮助资料
扫码关注网盛数新公众号,获取更多帮助资料
